In the global financial system, cross-border remittances have become an indispensable part of daily life and business operations. As the world economy grows and international trade expands, individuals and companies increasingly need to transfer funds to overseas bank accounts. While modern technology has simplified this process, the complexities of remittances—particularly when multiple financial institutions are involved—remain significant. Among these considerations, the use of SWIFT codes is critical. For instance, the SWIFT code NBEGEGCX004 for the National Bank of Egypt serves as a foundational element in facilitating secure and efficient cross-border transactions.
1. The Structure and Function of SWIFT Codes
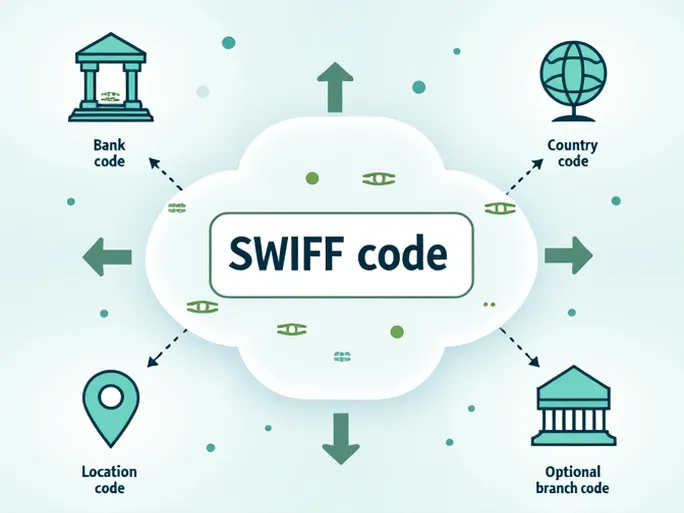
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) provides a unified communication platform and standardized coding system for banks and financial institutions worldwide. A SWIFT code, also known as a Bank Identifier Code (BIC), typically consists of 8 to 11 characters with a clear structure:
- Bank Code (4 letters): Identifies the financial institution (e.g., NBEG for the National Bank of Egypt).
- Country Code (2 letters): Specifies the bank’s location (e.g., EG for Egypt).
- Location Code (2 letters/numbers): Pinpoints the bank’s headquarters or primary branch (e.g., CX for Cairo).
- Branch Code (optional, 3 digits): Further refines the destination (e.g., 004 for a specific branch).
These codes serve not only as identifiers but also ensure the security and timely delivery of funds in cross-border transactions. For example, in the code NBEGEGCX004 , each segment plays a distinct role in routing payments accurately.
2. Common Challenges and Solutions in Cross-Border Transfers
While the SWIFT system offers efficiency, practical challenges such as delays, misrouted funds, or high fees may arise. To mitigate these risks, consider the following strategies:
- Verify Information: Double-check recipient details, including the SWIFT code, account number, and full name. Even minor errors can cause delays or failed transfers.
- Consult Customer Support: Contact the bank’s international remittance team to confirm requirements and clarify uncertainties.
- Compare Transfer Channels: Evaluate options like traditional banks or fintech services, which may offer lower fees or faster processing.
- Monitor Fees and Exchange Rates: Understand how fluctuating exchange rates and varying service charges impact the final amount received.
3. The Cross-Border Remittance Process: Key Steps
When using the SWIFT code NBEGEGCX004 , follow these steps to ensure a smooth transaction:
- Gather Documentation: Prepare identification, recipient details, and bank information.
- Complete the Transfer Form: Enter all data accurately, especially the SWIFT code.
- Review Before Submission: Scrutinize the form for errors.
- Submit and Track: Send the request to your bank and monitor the transfer’s progress.
4. Conclusion
Cross-border remittances are inherently complex, but understanding SWIFT codes—such as the National Bank of Egypt’s NBEGEGCX004 —enhances security and efficiency. By staying informed, verifying details, and leveraging professional guidance, individuals and businesses can navigate international transfers with confidence.