When initiating international wire transfers, many individuals encounter frustrating delays or errors. These issues frequently stem from misunderstandings about SWIFT/BIC codes—the essential identifiers that facilitate global banking transactions.
These alphanumeric codes, ranging from 8 to 11 characters, serve as unique fingerprints for financial institutions worldwide. Taking OTP BANKA D.D. as an example, we can examine how these codes function and why precision matters in cross-border payments.
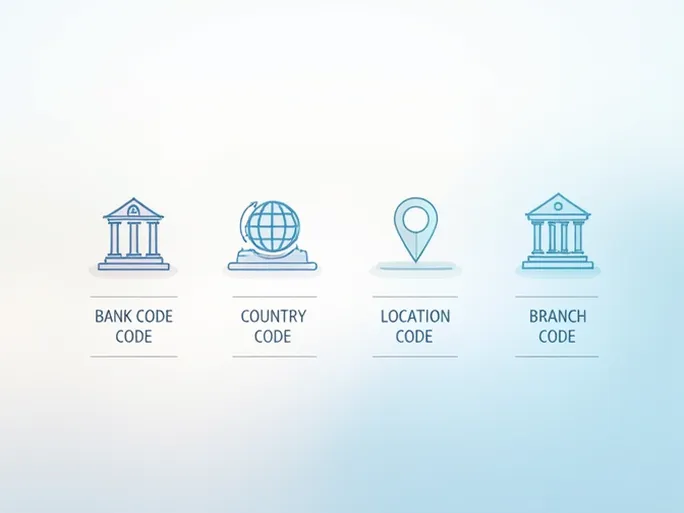
Every SWIFT/BIC code comprises four distinct components. The bank code (OTPV in our example) identifies the sending institution, followed by the country code (HR for Croatia). The location code (2X) pinpoints the bank's specific area, while the optional branch code (DUB) designates particular offices.
A critical detail often overlooked: when the final three characters appear as "XXX," this indicates the bank's headquarters rather than a specific branch. This distinction proves particularly important for international transactions, where routing funds to the correct destination requires exact coding.
Mismatched SWIFT/BIC codes create significant operational challenges. Transfers may disappear into banking limbo, funds can be delayed for weeks, and repeated errors may damage a customer's transaction history with financial institutions. Verifying these codes before initiating transfers remains the most effective safeguard against such complications.
Financial professionals emphasize that understanding SWIFT/BIC structure and function transforms international banking from a stressful necessity into a seamless process. As global transactions become increasingly commonplace, this knowledge empowers individuals and businesses to navigate international finance with confidence.