Commodity inspection has become an indispensable part of international trade, evolving into a core element of commercial transactions alongside global economic development. In recent years, with accelerated globalization, the scale of international trade has expanded significantly, and cross-border exchanges of goods have grown increasingly frequent. As a crucial mechanism for protecting consumer rights and ensuring fair trade, the importance of commodity inspection has become more prominent than ever. This necessitates a thorough understanding of its essence, necessity, and operational procedures.
I. Scope and Legal Basis of Commodity Inspection
The scope of commodity inspection is extensive, primarily governed by regulations outlined in the Commodity Inspection Law . The ultimate purpose of import/export commodity inspection is to guarantee transaction fairness and safety while ensuring product compliance. Standard inspections typically cover the following aspects:
- Quality : The fundamental attribute affecting consumer experience and safety. Inspectors employ chemical analysis and physical examination methods to rigorously evaluate raw materials and production processes against national or international standards.
- Specifications : Physical attributes including dimensions, weight, and capacity that directly impact market competitiveness. Inspectors verify these against manufacturer specifications and contractual requirements.
- Quantity and Weight : Critical factors in international transactions where inspectors verify actual shipment quantities against contractual agreements.
- Packaging : Affects both transportation safety and consumer first impressions. Inspections check for structural integrity and accurate labeling to prevent damage during handling.
- Safety and Hygiene : Particularly vital for food and pharmaceutical products, ensuring absence of harmful substances or microorganisms to protect public health.
The legal framework for inspection derives from three primary sources: contractual quality provisions in sales agreements, international/national standards, and relevant industry or corporate specifications.
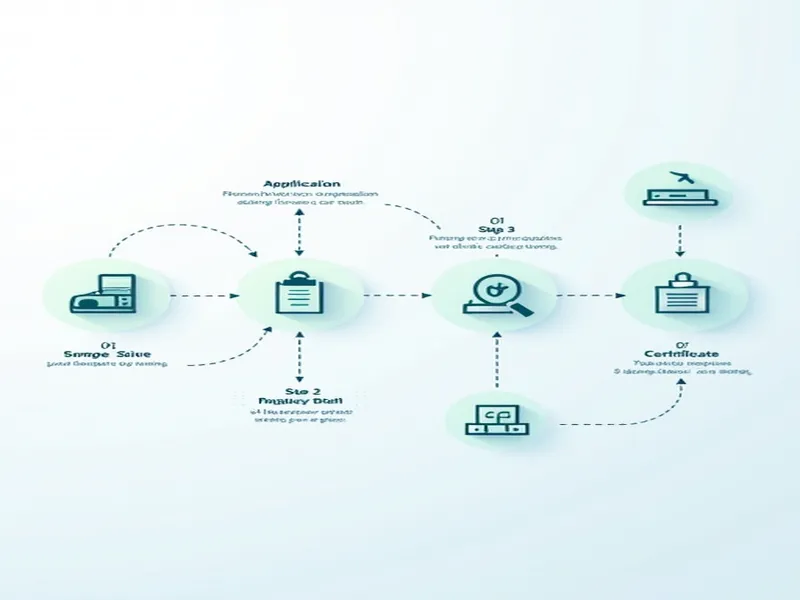
II. Operational Procedures for Import/Export Commodity Inspection
China's import/export inspection system operates through four standardized phases:
1. Inspection Application
Trading parties submit formal applications to local inspection authorities, including completed application forms specifying inspection requirements. Supporting documents such as sales contracts, sample products, invoices, and packing lists must accompany the submission.
2. Sampling
Upon approval, certified inspectors conduct on-site sampling at storage facilities using statistically valid methods to ensure representative samples. Strict protocols govern randomization and proportionality.
3. Testing and Analysis
Laboratories perform detailed examinations using modern instrumentation (e.g., colorimeters, gas chromatography) to verify quality, specifications, and packaging compliance. Both physical/chemical tests and sensory evaluations are conducted.
4. Certification
For compliant exports, authorities issue release documents or customs clearance stamps. Import certifications include "Inspection Notifications" or formal certificates for settlement purposes. Notably, recipients may file claims within stipulated periods if defects are discovered during initial acceptance inspections.
III. Strategic Importance in Global Commerce
Commodity inspection serves multiple critical functions in international trade:
- Consumer Protection : Ensures product reliability and truthful information disclosure, building market trust while enhancing brand reputation.
- Market Integrity : Prevents substandard goods from distorting competition, fostering sustainable trade ecosystems.
- Operational Efficiency : Accelerates market circulation of compliant goods while reducing quality-related disputes and returns.
- National Reputation : Compliance with international standards elevates product competitiveness and projects positive national image.
IV. Future Evolution and Technological Integration
The inspection landscape faces transformative changes as globalization advances:
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and big data analytics will enable more precise risk assessment and quality monitoring, significantly improving inspection accuracy and efficiency. Simultaneously, expanding cross-border trade will drive international standardization of inspection protocols, facilitating greater global cooperation.
In our increasingly interconnected world, strengthening inspection frameworks and technological innovation becomes paramount for sustaining international trade growth. Through continued education and awareness, stakeholders can better appreciate inspection's pivotal role in maintaining stable, healthy global commerce.
Properly implemented commodity inspection promises to make future international trade safer, more transparent, and increasingly efficient - injecting renewed vitality into worldwide economic development.