In today's globalized business environment, cross-border logistics has become the critical bridge connecting enterprises to international markets. Whether for e-commerce platforms or traditional trading companies, mastering efficient cross-border logistics has emerged as the key differentiator between success and failure. Far from being a simple transportation process, cross-border logistics represents a complex and challenging system engineering project. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of each stage in the cross-border logistics chain, examining processes, key considerations, and future trends to help businesses establish firm footing in competitive international markets.
1. Order Confirmation and Inventory Preparation: The Foundation of Precision Management
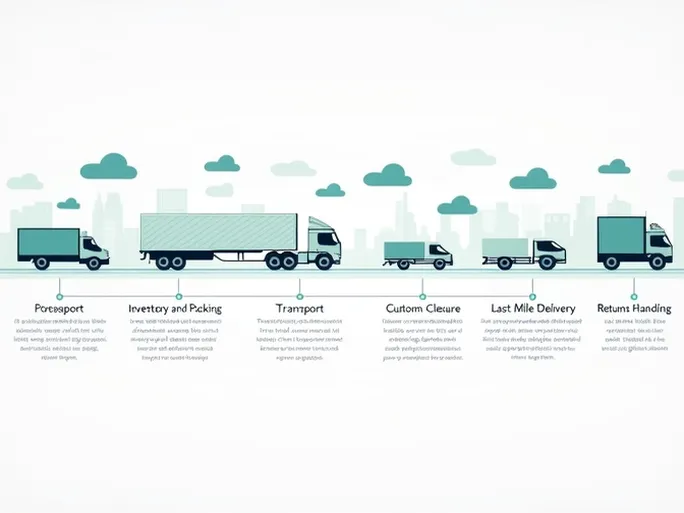
The cross-border commerce journey begins with order confirmation and inventory preparation. The moment a customer places an order, businesses must respond swiftly to ensure accurate and timely fulfillment. During peak sales seasons, real-time inventory updates become particularly crucial. Sellers must implement meticulous inventory management systems for their products.
Beyond quality inspections, packaging compliance represents another critical consideration. Product packaging must not only be visually appealing but also meet destination country regulations. For instance, some nations mandate specific requirements for electronic products—including anti-static packaging and compulsory labeling with instructions. Businesses must thoroughly understand these regulations during preparation to avoid complications in subsequent processes.
Modern management systems like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and WMS (Warehouse Management Systems) have become indispensable tools for maintaining seamless information and logistics coordination throughout this stage.
2. Goods Consolidation and Warehouse Management: The Pillars of Operational Efficiency
Following inventory preparation, products must be consolidated into designated warehouses. Effective warehouse management during this phase significantly enhances distribution efficiency. Basic warehouse functions include quality inspection, registration, and categorization of incoming goods to ensure order compliance and prevent returns or disputes.
Businesses must implement scientific inventory management strategies, adopting principles like FIFO (First-In-First-Out) or LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) according to product characteristics. Many e-commerce businesses now utilize overseas warehouse models—establishing storage facilities in importing countries to enable localized distribution. This approach dramatically reduces delivery times, improves customer satisfaction, and lowers overall logistics costs while enhancing supply chain efficiency.
3. Transportation Mode Selection: Balancing Cost and Efficiency
Selecting optimal transportation modes requires careful consideration of multiple factors including product characteristics, delivery timelines, and cost structures. Primary cross-border shipping options include:
- Ocean Freight: The most economical choice for bulk shipments, though with longer transit times (typically weeks).
- Air Freight: Ideal for time-sensitive goods, delivering within days despite higher costs.
- Rail Transport: A cost-effective middle ground gaining popularity in Eurasian trade corridors.
- International Express: Services like DHL, UPS, and FedEx offer unparalleled speed for small parcels at premium rates.
Businesses increasingly employ multimodal transportation strategies, combining different methods to optimize efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
4. Shipment Tracking: Ensuring Transparency Throughout Transit
Real-time shipment tracking has become standard practice, with advanced systems allowing sellers and customers to monitor progress from dispatch through delivery. Key tracking information includes origin details, loading status, transit updates, and estimated arrival times.
This transparency significantly reduces customer anxiety—particularly important in cross-border transactions where logistics concerns frequently influence purchasing decisions. For sellers, providing precise tracking information enhances brand reputation and facilitates customer relationship management.
5. Customs Clearance: Navigating Regulatory Complexities
Customs procedures represent perhaps the most intricate yet critical phase in cross-border logistics. Businesses must maintain thorough understanding of both export regulations and destination country import policies to prevent shipment delays. Required documentation typically includes customs declarations, commercial invoices, packing lists, and various certificates of compliance.
Many enterprises now engage professional customs brokerage services to navigate this complex landscape. Compliance errors can result in detained shipments, damaged goods, or financial penalties—making regulatory adherence essential for protecting business interests and ensuring smooth international trade operations.
6. Destination Warehousing and Sorting: Optimizing Last-Mile Efficiency
Following customs clearance, goods proceed to destination warehouses for receiving, sorting, and final preparation. With order volumes growing exponentially, businesses increasingly implement automated sorting systems and intelligent logistics tools to minimize human error and maximize processing speed.
Real-time inventory monitoring systems have become indispensable for maintaining operational flexibility and reducing customer wait times. Leading cross-border retailers now adjust warehousing strategies based on seasonal factors like climate variations and holiday periods to guarantee prompt deliveries during critical periods.
7. Last-Mile Delivery: The Customer Experience Frontier
The final delivery leg presents both the greatest challenge and most significant opportunity in cross-border logistics—directly impacting consumer satisfaction. Businesses must develop sophisticated delivery solutions to navigate urban traffic complexities and meet tight delivery windows.
Modern options include traditional courier services, self-pickup locations, and smart parcel lockers—the latter two offering customers greater flexibility in retrieval timing. Some retailers now provide premium services like scheduled deliveries and real-time shipment notifications to enhance convenience and reduce waiting anxiety.
8. Returns Processing and Customer Service: Building Trust Through Support
With cross-border return rates typically exceeding domestic e-commerce averages, efficient returns management has become crucial for customer retention. Clear return policies and streamlined processes—from initiation to refund/exchange—are essential. Many businesses now maintain dedicated customer service teams and implement specialized returns management systems to handle these processes efficiently.
Exceptional post-purchase service not only boosts satisfaction but also strengthens brand reputation. As consumers increasingly prioritize after-sales experience, superior customer support has emerged as a key differentiator for sustainable business growth.
Key Challenges in Cross-Border Logistics
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating diverse international customs regulations
- Delivery Speed: Balancing security with efficiency
- Information Transparency: Maintaining shipment visibility
- Cost Optimization: Strategic transportation mode selection
- Risk Management: Mitigating potential losses or delays
The Future of Cross-Border Logistics
Technological innovation continues reshaping the logistics landscape:
- Smart Warehousing: AI and robotics driving automated sorting and fulfillment
- Blockchain Integration: Enhancing transparency and security across supply chains
- Sustainable Logistics: Eco-friendly packaging and transportation solutions
- Integrated Services: Comprehensive solutions spanning customs, warehousing, and delivery
Conclusion
Mastering cross-border logistics—from order fulfillment through returns management—requires deep expertise and practical experience. In today's global trade environment, businesses that optimize their logistics operations gain decisive competitive advantages. This comprehensive guide provides the foundational knowledge enterprises need to navigate international markets successfully, creating new opportunities and delivering exceptional customer value worldwide.