In today's increasingly competitive market landscape, efficient supply chain operations have become crucial for business success. As the critical nexus between information flow and physical logistics, warehouses require particularly refined and efficient task management systems. How can companies optimize complex and ever-changing warehouse operations to achieve fast and accurate goods movement? This article provides an in-depth analysis of warehouse task management optimization, offering practical solutions for businesses.
Understanding Warehouse Task Management
Effective warehouse operations depend on well-organized daily responsibilities, task execution, and information exchange—all of which directly impact the speed and accuracy of goods movement. Without proper management systems, companies face resource waste, operational delays, and costly errors. Proper task management not only enhances resource allocation efficiency but also enables standardized operations.
The primary goal of warehouse task management is achieving precision and efficiency through optimal resource allocation—including labor, equipment, and time. During peak periods, for example, management systems must dynamically adjust resources to prioritize urgent orders while maintaining normal operations. Appropriate strategies prevent order delays and facilitate subsequent task completion.
The Strategic Value of Task Management
Modern warehouses increasingly rely on digital and automated technologies, which elevate management intelligence while reducing errors caused by information delays. Through integrated Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), companies achieve significantly improved execution accuracy and response capabilities for various tasks.
Strategically, warehouse task management extends beyond internal process optimization—it's a powerful tool for enhancing service levels and overall competitiveness. With customers demanding faster and more accurate deliveries, proper resource allocation and process optimization through task management helps companies meet complex market demands while ultimately increasing customer satisfaction.
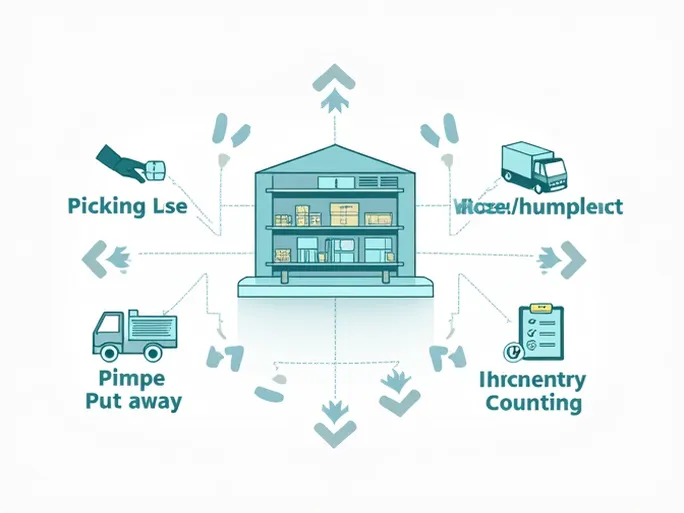
Key Warehouse Task Types
1. Order Picking
The most time-critical warehouse operation, order picking directly impacts delivery speed. Methods like zone picking or batch picking accommodate different order volumes, with efficiency gains coming from selecting the right approach for specific business needs.
2. Replenishment
This task maintains adequate inventory in picking areas, typically performed during off-peak hours to avoid space waste from overstocking. Smart replenishment systems use data forecasting to optimize the process.
3. Put-away
Efficiently storing incoming goods in predetermined locations reduces picking and replenishment workloads. Technologies like automated conveyors significantly enhance this operation.
4. Inventory Counting
Stock verification processes benefit from strategic approaches and technologies like RFID or drones, improving both speed and accuracy.
Optimizing Task Management Processes
Effective task management flows through four critical phases—all requiring efficient information sharing and real-time feedback to ensure optimal coordination:
Task Allocation
The starting point involves dynamic adjustments based on task nature, priority, and available resources. Urgent tasks during peak periods must receive priority without disrupting regular operations.
Task Execution
Combining efficiency with accuracy, standardized procedures minimize human error risks. Real-time technical guidance supports employees during this phase.
Task Tracking
Continuous monitoring enables timely adjustments, preventing delays from cascading through operations.
Feedback Mechanisms
By monitoring and evaluating key metrics, companies gather data to inform future task planning and optimization.
Challenges and Optimization Strategies
Warehouse task management faces several challenges—from balancing priorities and resource allocation to technological limitations. Addressing these requires both technical solutions and managerial insight.
Key optimization strategies include:
1. Technology-Driven Solutions
Implementing WMS enables task automation and optimization, adapting quickly to market changes while maximizing efficiency.
2. Process Optimization
Standardized procedures and rules reduce wasted effort and operational variance, creating efficient task execution chains.
3. Workforce Management
Scientific human resource approaches—including skills training and incentive programs—boost team efficiency and motivation.
Case Study: Successful Implementation
E-commerce company A demonstrated successful warehouse optimization by implementing a WMS, achieving efficient information flow that resolved resource allocation issues and priority conflicts. Within six months, they reported significant improvements in task accuracy, picking time reduction, and overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Modern warehouse task management represents a comprehensive process involving multiple operational dimensions. Through refined management approaches, companies can gain competitive advantages, enhance customer service levels, and drive sustainable business growth.