China's customs duty exemption and reduction classification system categorizes different approaches to tax management for imported and exported goods. This system aims to enhance the transparency and efficiency of tariff collection. By properly classifying various import and export goods, customs authorities can more effectively administer duty reduction and exemption policies while providing robust support for subsequent data analysis and statistics.
I. Classification of Duty Exemption and Reduction Categories
The system primarily divides duty treatments into five categories: statutory regular taxation, statutory duty reduction/exemption, special duty reduction/exemption, other duty reductions/exemptions, and provisional tariff rates. The special duty reduction/exemption category is further subdivided based on regional policies, intended use, trade nature, enterprise characteristics, and funding sources.
II. Coding Structure for Duty Exemption/Reduction Categories
The classification system employs a three-digit numerical code. The first digit indicates the broad category, while the second and third digits specify the sequential order of duty reduction/exemption items within that category.
III. Category Codes and Their Applications
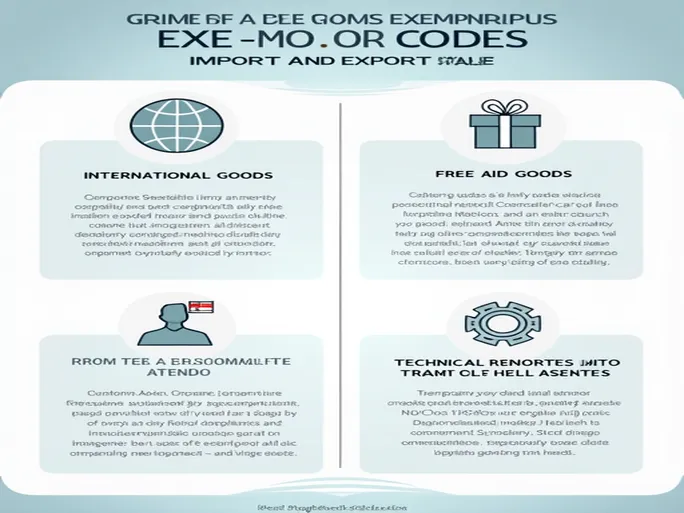
1. General Taxation for Import/Export Goods
Definition: Goods subject to regular customs duties, value-added tax, and other charges as stipulated by relevant laws and regulations.
Code: 101 (General Taxation)
Application: Includes all taxable items not otherwise specified.
2. Gratuitous Aid Import/Export Materials
Definition: Materials provided as non-commercial gifts from foreign governments or international organizations.
Code: 201 (Gratuitous Aid)
Application: Includes materials provided under bilateral gratuitous aid agreements, supplies from UN organizations, and China's outward gratuitous aid items.
3. Other Statutory Duty Reduction/Exemption Goods
Definition: Goods eligible for statutory duty reductions/exemptions excluding gratuitous aid items.
Code: 299 (Other Statutory)
Application: Includes export refunds, replacement goods without cost, and goods damaged by force majeure.
4. Special Economic Zone Import Materials and Export Goods
Definition: Duty reduction policies for materials imported for self-use and export products in designated special economic zones.
Code: 301 (Special Zones)
Application: Includes self-use materials for enterprises and qualified export products within these zones.
5. Bonded Zone Import Materials
Definition: Materials imported for use within bonded zones under special duty reduction policies.
Code: 307 (Bonded Zones)
Application: Includes infrastructure construction materials and enterprise equipment for self-use within bonded zones.
6. Scientific and Educational Imports
Definition: Materials imported by designated research institutions and educational establishments to promote science and education.
Code: 401 (Scientific/Educational)
Application: Includes imports by State Council-designated research institutions and educational units.
7. Enterprise Technological Transformation Imports
Definition: Advanced technology and equipment imported to facilitate enterprise technological upgrades.
Code: 403 (Technological Transformation)
Application: Includes essential equipment for approved technological transformation projects.
8. National Major Project Imports
Definition: Equipment required for major construction projects approved by the state.
Code: 406 (Major Projects)
Application: Includes imports for State Council-approved major projects.
9. Exceptional Duty Reduction/Exemption Goods
Definition: Import/export goods that cannot be classified under any other category.
Code: 999 (Exceptional)
This classification system provides clear insight into how China's customs duty exemption and reduction codes operate and their impact on import/export management. The effective implementation of these policies not only supports national fiscal revenue but also guides enterprises toward compliant operations in international trade, promoting healthy economic development. The detailed classification and rigorous review process by customs authorities play crucial roles in this system.